
Aenean ornare velit lacus, ac varius enim lorem ullamcorper dolore aliquam.
Kesterite-based solar cells manufactured using thin film technologies have the advantage of being cost-effective and being a possible long-term solution for the replacement of Silicon-based cells. For synthesizing the CZTS layer, initially, Zn/Sn/Cu were deposited using Magnetron sputtering and Thermal Evaporation systems followed by the requirement for sulfurization to obtain Kesterite.
An in-house sulfurization setup was developed at the Non-Ferrous Materials Technology Development Centre (NFTDC) to synthesize Kesterite solar cells. The literature was studied extensively to find the right setup, the set-up was designed using CATIA V5 and then manufactured. Initially, a quartz tubing was used but later it was changed to ceramic tubing as the quartz tube was not durable enough. Kesterite-based solar cells of dimension 50 mm * 50 mm were developed using this setup.
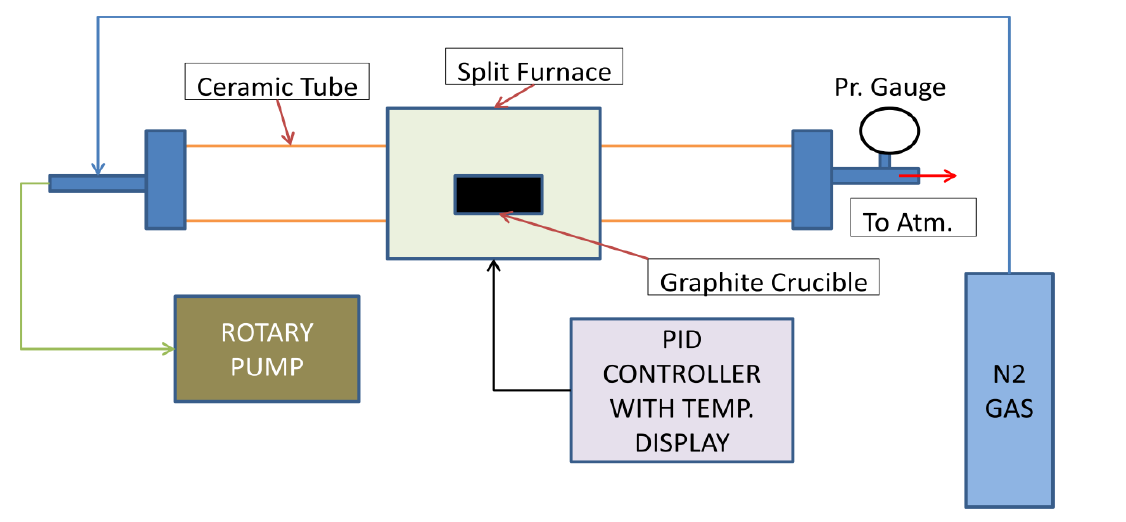
The setup includes a ceramic tube and a graphite crucible designed in such a way that there is a provision to keep sulfur and the substrate. A separator with pinholes was used to separate the substrate and sulfur. The graphite crucible can withstand high thermal shock and temperature up to 1500ᵒC. The maximum cell size that can be synthesized is 50 mm * 50 mm.
The sulfurization set up was designed using CATIA V5 3D modeling software.
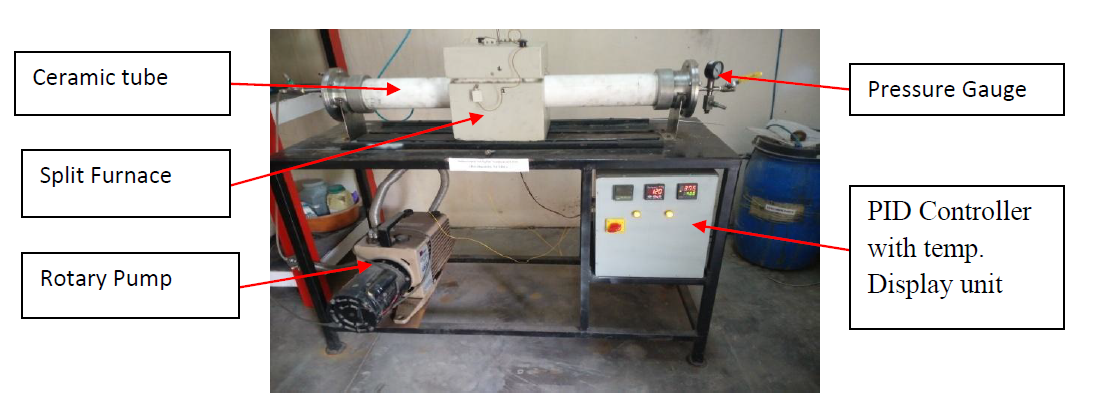
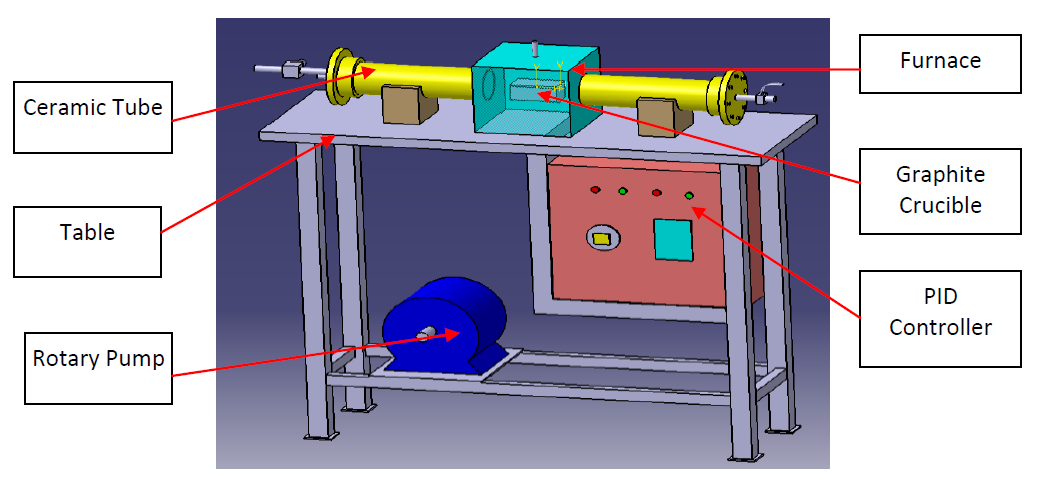

After assembling the Sulfurization setup, the parameters for sulfurization were optimized. The temperature of sulfurization and the time for the formation of CZTS were the main parameters that were determined by keeping the window for the formation of secondary phases out.